Federated States of Micronesia
| Federated States of Micronesia | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: Peace Unity Liberty | ||||||
| Anthem: Patriots of Micronesia |
||||||
 |
||||||
| Capital | Palikir |
|||||
| Largest city | Weno | |||||
| Official language(s) | English (national; local languages are used at state and municipal levels) | |||||
| Demonym | Micronesian | |||||
| Government | Democratic Federated Presidential Republic | |||||
| - | President | Manny Mori | ||||
| - | Vice President | Alik L. Alik | ||||
| Independence | from US-administered UN Trusteeship | |||||
| - | Date | 3 November 1986 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 702 km2 (188th) 271 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2009 estimate | 111,000[1] (181st) | ||||
| - | 2000 census | 107,000 | ||||
| - | Density | 158.1/km2 (66th) 409.6/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2002 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $277 million (215th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $2,000 (180th) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | n/a (unranked) (n/a) | |||||
| Currency | United States dollar (USD) |
|||||
| Time zone | (UTC+10 and +11) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC+10 and +11) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .fm | |||||
| Calling code | 691 | |||||
| 1 | GDP is supplemented by grant aid, averaging around $100 million annually (2002 estimate). | |||||
| 2 | 2002 estimate. | |||||
The Federated States of Micronesia /ˌmaɪkroʊˈniːʒə/ is an independent, sovereign island nation, made up of four states from west to east: Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae. It comprises approximately 607 small islands in the Western Pacific spread over almost 1,700 miles (2,700 km) longitudinally just north of the equator some 2,500 miles (4,000 km) southwest of the main islands of Hawaii and about 1,800 miles (2,900 km) north of eastern Australia, lying northeast of New Guinea, south of Guam and the Marianas, west of Nauru and the Marshalls, and east of Palau and the Philippines.
While the FSM's total land area is quite small, amounting to approximately 270 square miles (700 km2), it occupies more than 1,000,000 square miles (2,600,000 km2) of the Pacific Ocean. The capital is Palikir, the largest city Kolonia, both on Pohnpei.
Each of its four States is centered around one or more main high islands, and all but Kosrae include numerous outlying atolls. The Federated States of Micronesia is spread across part of the Caroline Islands in the wider region of Micronesia, which consists of thousands of small islands divided between several countries. The term Micronesia may refer to the Federated States or to the region as a whole.
The FSM was formerly a part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI), a United Nations Trust Territory under U.S. administration, but formed its own constitutional government on May 10, 1979, so becoming a sovereign state after independence was attained on November 3, 1986 under a Compact of Free Association with the United States. Other neighboring island entities, and also former members of the TTPI, formulated their own constitutional governments and became the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI) and the Republic of Palau (ROP). The FSM has a seat in the United Nations.
Contents |
History
The ancestors of the Micronesians settled over four thousand years ago. A decentralized chieftain-based system eventually evolved into a more centralized economic and religious empire centered on Yap.
Nan Madol, consisting of a series of small artificial islands linked by a network of canals, is often called the Venice of the Pacific. It is located near the island of Pohnpei and used to be the ceremonial and political seat of the Saudeleur dynasty that united Pohnpei's estimated 25,000 people from about AD 500 until 1500, when the centralized system collapsed.
European explorers—first the Portuguese in search of the Spice Islands (Indonesia) and then the Spanish—reached the Carolines in the sixteenth century, with the Spanish establishing sovereignty. It was sold to Germany in 1899, conquered by Japan in 1914, and later by the United States during World War II and administered by the US under United Nations auspices in 1947 as part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands.
During World War II, a significant portion of the Japanese fleet was based in Truk Lagoon. In February 1944, Operation Hailstone, one of the most important naval battles of the war, took place at Truk, in which many Japanese support vessels and aircraft were destroyed.
On May 10, 1979, four of the Trust Territory districts ratified a new constitution to become the Federated States of Micronesia. Palau, the Marshall Islands, and the Northern Mariana Islands chose not to participate. The FSM signed a Compact of Free Association with the United States of America, which entered into force on November 3, 1986, marking Micronesia's emergence from trusteeship to independence. The Compact was renewed in 2004.
Politics
The Federated States of Micronesia is governed by the 1979 constitution, which guarantees fundamental human rights and establishes a separation of governmental powers. The unicameral Congress has fourteen members elected by popular vote. Four senators—one from each state—serve four-year terms; the remaining ten senators represent single-member districts based on population, and serve two-year terms. The President and Vice President are elected by Congress from among the four state-based senators to serve four-year terms in the executive branch. Their congressional seats are then filled by special elections.
The president and vice president are supported by an appointed cabinet. There are no formal political parties.
In international politics, the Federated States of Micronesia has often voted with the United States with respect to United Nations General Assembly resolutions.[2]
Administrative divisions
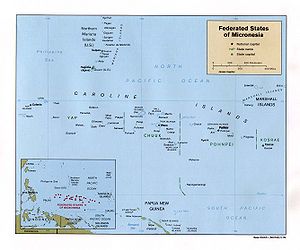
The four states in the federation are:
| Flag | State | Capital | Land area km²[3] |
Population[4] | Population density per km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chuuk | Weno | 127 | 54,595 | 420 | |
| Kosrae | Tofol | 110 | 9,686 | 70 | |
| Pohnpei | Kolonia | 346 | 34,685 | 100 | |
| Yap | Colonia | 118 | 16,436 | 95 |
These states are further divided into municipalities.
Geography

The Federated States of Micronesia consists of 607 islands extending 1,800 miles (2,900 km) across the archipelago of the Caroline Islands east of the Philippines. The four constituent island groups are Yap, Chuuk (called Truk until January 1990), Pohnpei (known as "Ponape" until November 1984), and Kosrae (formerly Kusaie). These four states are each represented by a white star on the national flag. The capital is Palikir, on Pohnpei.
The country has seven official languages: English, Ulithian, Woleaian, Yapese, Pohnpeian, Kosraean, and Chuukese.
The other languages spoken in the country are Pingelapese, Ngatikese, Satawalese, Kapingamarangi Language, Nukuoro Language, Puluwatese, Mortlockese, and Mokilese.
Economy
Economic activity in the Federated States of Micronesia consists primarily of subsistence farming and fishing. The islands have few mineral deposits worth exploiting, except for high-grade phosphate. Long line tuna fishing is also viable with foreign vessels from China operated in the 1990s. The potential for a tourist industry exists, but the remoteness of the location and a lack of adequate facilities hinder development. Financial assistance from the US is the primary source of revenue, with the US pledged to spend $1.3 billion in the islands in 1986–2001. Geographical isolation and a poorly developed infrastructure are major impediments to long-term growth.
The nation uses the US dollar as its currency.
Transportation
The Federated States of Micronesia is served by four international airports.
- Pohnpei International Airport in the main island of the state of Pohnpei
- Chuuk International Airport located in the main island of the state of Chuuk
- Kosrae International Airport located in the main island of the state of Kosrae
- Yap International Airport located in the main island of the state of Yap
Demographics
The indigenous population of the Federated States of Micronesia, which is predominantly Micronesian, consists of various ethnolinguistic groups. It has a nearly 100% Pacific Islander and Asian population. Chuukese 48.8%, Pohnpeian 24.2%, Kosraean 6.2%, Yapese 5.2%, Yap outer islands 4.5%, Asian 1.8%, Polynesian 1.5%, other 6.4%, unknown 1.4%. A sizeable minority also have some Japanese ancestry, which is a result of intermarriages between Japanese settlers and Micronesians during the Japanese colonial period.[5]
There is also growing expatriate population of Americans, Australians, Europeans, and residents from China and the Philippines since the 1990s. English has become the common language of the government, and for secondary and tertiary education. Outside of the main capital towns of the four FSM states, the local languages are primarily spoken. Population growth remains high at more than 3% annually, offset somewhat by net emigration. Pohnpei is notable for the prevalence of the extreme form of color blindness known as maskun.
Culture

Each of the four States has its own culture and traditions, but there are also common cultural and economic bonds that are centuries old. For example, cultural similarities like the importance of the traditional extended family and clan systems can be found on all the islands.
The island of Yap is notable for its "stone money" (Rai stones), large disks usually of calcite, up to 12 feet (4 m) in diameter, with a hole in the middle. The islanders, aware of the owner of a piece, do not necessarily move them when ownership changes. There are five major types: Mmbul, Gaw, Ray, Yar, and Reng, the last being only 1 foot (30 cm) in diameter. Their value is based on both size and history, many of them having been brought from other islands, as far as New Guinea, but most coming in ancient times from Palau. Approximately 6,500 of them are scattered around the island.
Languages
The languages of the Federated States of Micronesia include English (the official and common language), Trukese, Pohnpeian, Yapese, Kosraean.[6] There are also about 3,000 speakers of Kapingamarangi and Ulithian, and under 1,000 speakers of Nukuoro.
Literature
There have been few published literary writers from the Federated States of Micronesia.[7] In 2008, Emelihter Kihleng became the first ever Micronesian to publish a collection of poetry in the English language[8].
Religion
Defense and foreign affairs
The FSM is a sovereign, self-governing state in free association with the United States, which is wholly responsible for its defense. The Division of Maritime Surveillance operates a paramilitary Maritime Wing and a small Maritime Police Unit. The Compact of Free Association allows FSM citizens to join the U.S. military without having to obtain U.S. permanent residency or citizenship,[9] allows for immigration and employment for Micronesians in the U.S., and establishes economic and technical aid programs.
See also
- Index of Federated States of Micronesia-related articles
Notes
- ↑ Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2009) (.PDF). World Population Prospects, Table A.1. 2008 revision. United Nations. http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/wpp2008/wpp2008_text_tables.pdf. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
- ↑ General Assembly - Overall Votes - Comparison with U.S. vote lists Micronesia as in the country with the fourth high coincidence of votes. Micronesia has always been in the top four.
- ↑ FSM government website - Geography
- ↑ FSM government website - Population
- ↑ President Emanuel Mori Meets With Japan Prime Minister Yasuo Fukuda; AESonline.org Government of the Federated States of Micronesia, December 12, 2007
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
- ↑ "Seeking Micronesian literary writers", Marianas Variety, February 18, 2009
- ↑ "Micronesian Poet Publishes Collection of Poems", Office of Insular Affairs, May 12, 2008
- ↑ U.S. Military Enlistment Standards
References
- US-CIA. CIA - The World Factbook: Federated States of Micronesia. The World Factbook. United States of America: Central Intelligence Agency. 2003.
- History_Federated_States_of_Micronesia
- Meet The Parents [1]
Bibliography
- Brower, Kenneth; Harri Peccinotti (1981). Micronesia: The Land, the People, and the Sea. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0807109924.
- Darrach, Brad; David Doubilet (1995). "Treasured Islands". Life (August 1995): 46–53.
- Falgout, Suzanne (1995). "Americans in Paradise: Anthropologists, Custom, and Democracy in Postwar Micronesia". Ethnology (Ethnology, Vol. 34, No. 2) 34 (Spring 1995): 99–111. doi:10.2307/3774100. http://jstor.org/stable/3774100.
- Friedman, Hal M. (1993). "The Beast in Paradise: The United States Navy in Micronesia, 1943–1947". Pacific Historical Review 62 (May 1993): 173–195.
- Friedman, Hal M. (1994). "Arguing over Empire". Journal of Pacific History 29 (1994): 36–48. doi:10.1080/00223349408572757.
- Hanlon, David (1998). Remaking Micronesia: Discourses over Development in a Pacific Territory, 1944–1982. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0824818946.
- Hezel, Francis X. (1995). "The Church in Micronesia". America 18 (February 1995): 23–24.
- Kluge, P. F. (1991). The Edge of Paradise: America in Micronesia. New York: Random House. ISBN 0394581784.
- Malcomson, S. L. (1989). "Stranger than Paradise". Mother Jones 14 (January 1989): 19–25.
- "Micronesia: A New Nation". U.S. News & World Report (October 15, 1984): 80–81.
- Parfit, Michael (2003). "Islands of the Pacific". National Geographic 203 (March 2003): 106–125.
- Patterson, Carolyn Bennett (1986). "In the Far Pacific: At the Birth of Nations". National Geographic 170 (October 1986): 460–500.
- Peoples, James G. (1993). "Political Evolution in Micronesia". Ethnology (Ethnology, Vol. 32, No. 1) 32 (Winter 1993): 1–17. doi:10.2307/3773542. http://jstor.org/stable/3773542.
- Rainbird, Paul (2003). "Taking the Tapu: Defining Micronesia by Absence". Journal of Pacific History 38 (September 2003): 237–250. doi:10.1080/0022334032000120558.
- Schwalbenberg, Henry M.; Thomas Hatcher (1994). "Micronesian Trade and Foreign Assistance". Journal of Pacific History 29 (1): 95–104. doi:10.1080/00223349408572762.
External links
- Government
- General information
- Federated States of Micronesia entry at The World Factbook
- Federated States of Micronesia from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Federated States of Micronesia at the Open Directory Project
- Jane's Federated States of Micronesia Home Page
- Trust Territory of the Pacific Archives at the University of Hawaii
- Pacific Islands Legal Information Institute - Federated States of Micronesia
- Nature.org - Micronesia environmental conservation
- myMicronesia.com Online resource center about the islands of Micronesia. Provides free listings and links to all Micronesian businesses, as well as civic, cultural, health and educational organizations.
- Habele.org - Outer Islands Information about the remote islands and atolls outside the four state capitals of Micronesia from an educational nonprofit.
- News media
- The Yap Networker – Yap's news source
- Maps
- Wikimedia Atlas of the Federated States of Micronesia
- Map of Micronesia
- Nan Madol islet complex Provides computer based reconstruction of the main islets and features
- Travel
- Federated States of Micronesia travel guide from Wikitravel
- Moon Handbooks Micronesia
- Travel Overview of Micronesia
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

